Wind energy is a clean, eco-friendly, and renewable source of energy.
For centuries, wind has been a driving force for humanity. In the past, it helped us cross oceans, grind grain, and drain land. Today, it plays a crucial role in transitioning to an eco-friendly and climate-conscious energy source.
Wind turbines are typically grouped together in wind farms or wind energy plants in windy areas to produce electricity on a large scale.
How Does a Wind Turbine Work?
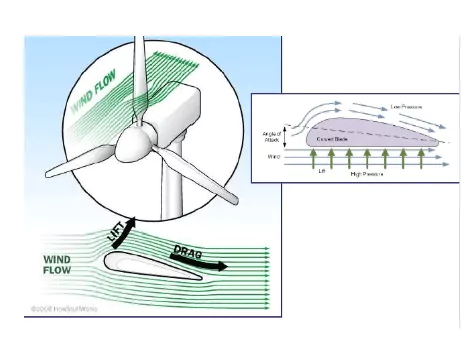
Wind turbines operate on a simple principle. Wind strikes the rotor blades. The combination of wind speed and blade rotation creates a pressure distribution on the blades. This pressure distribution generates a torque. The torque causes the shaft to rotate. The shaft is connected to a generator that produces electrical power.
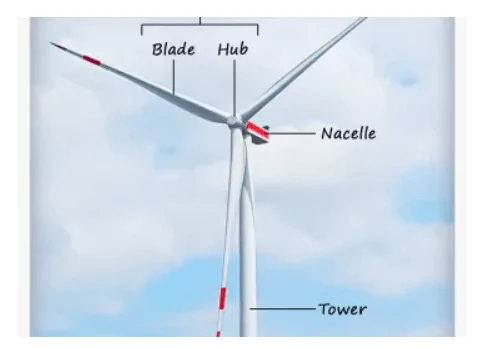
Main Components of a Wind Turbine
The main components of a wind turbine are listed below:
- Wind turbine rotor, includes blades and center shaft.
- Wind turbine nacelle, houses the gearbox and the generator.
- Wind Turbine Tower
Wind Turbine Rotor
The wind turbine rotor consists of the wind turbine blades and the central shaft.
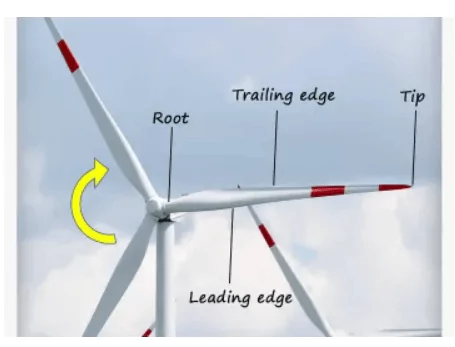
Wind Turbine Blades
Wind turbine blades are a critical component in the system when extracting kinetic energy from the wind. The blades are designed in such a way that aerodynamic forces are generated when wind passes over them, causing them to rotate and generate torque.
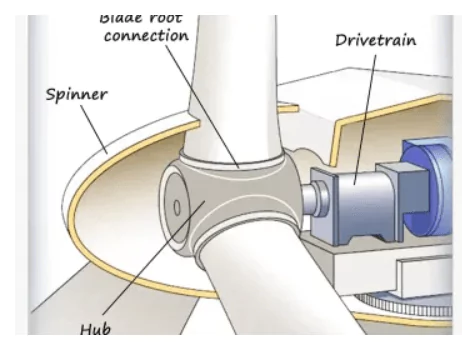
Wind Turbine Center Shaft (Hub)
The center shaft is the central connection point connecting the three blades. The center shaft is covered by a rotating cover to protect it from external influences.
Wind Turbine Nasel (Machine Room)
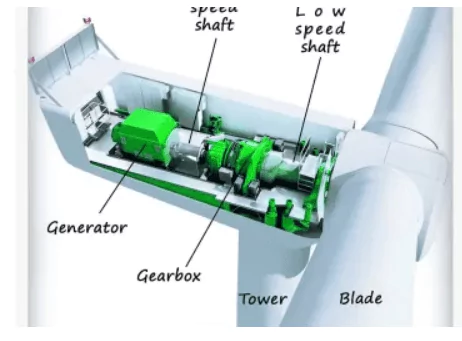
The nacelle is the housing that contains all the electrical, mechanical, and control components of the wind turbine system and is positioned on top of the tower.
The rotational energy of the wind turbine blades is transferred directly to the low-speed shaft. However, the rotation of the low-speed shaft alone is not sufficient for the generator to produce electricity. Therefore, a gearbox is used to convert the low RPM (revolutions per minute) to high RPM, which is then transferred to the high-speed shaft.
Wind Turbine Tower
The tower is the main structural support for the nacelle and the wind turbine rotor. It consists of cylindrical steel sections that are bolted together. This type of tower is commonly referred to as a tubular steel tower. In addition to steel, towers can also be made of concrete, as in fully concrete towers, or a combination of steel and concrete, known as hybrid towers.
Types of Wind Energy
Wind energy is divided into two types:
- On Shore Wind Energy
- Off Shore Wind Energy
Wind Energy Conversion Factors
The amount of energy transferred from the wind to wind turbines depends mainly on three main factors:
- Wind Speed
- Wind Turbine Blade Size
- Air Density
Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy offers numerous advantages and benefits compared to traditional energy sources:
- It is a clean energy source and does not cause air pollution like fossil fuels.
- It is a renewable energy source and does not deplete natural resources.
- Wind is a free and widely available resource around the world.
- Electricity generated from wind energy is cost-effective and economical.
- Wind energy creates employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Wind energy is safe and reliable.
- Wind energy has minimal environmental impact.
- It contributes to sustainable development.